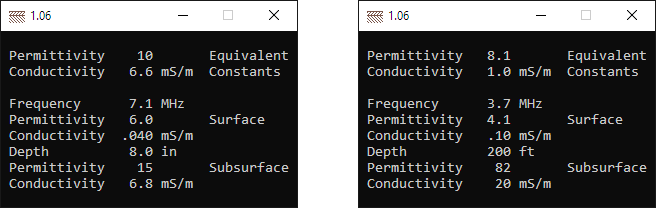

8″ of concrete over pastoral ground Water table 200′ below desert
Ever wonder how the concrete house foundation might affect your rooftop antenna? How about the asphalt driveway below your dipole? Could a foot of snow affect your backyard vertical? What about the water table your neighbor insists is 15 feet down?
This Windows program determines equivalent ground constants for such situations. It calculates the complex reflection coefficient for RF power incident vertically on stratified ground with two layers. Then it finds constants for single-layer ground with the same coefficient. If two ground models appear identical when illuminated by RF from above, they should yield the same antenna currents, input impedance, and ground loss.
One limitation is that an equivalent may not exist for some situations. Another is that equivalence may not be valid for radiation patterns when power incidence is far from vertical. Finally, results have not been verified.
The documentation includes typical permittivity and conductivity values for snow, ice, asphalt, and concrete. Generic values for soil and water are here.
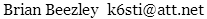 88–108 MHz
88–108 MHz